Today’s beauty market offers countless skincare solutions, and among them, the horse placenta drink has emerged as one of the most popular new beauty trends trusted by many women. Horse placenta is known as a rich source of nutrients, including proteins, vitamins, minerals, amino acids, and growth factors, providing a wide range of benefits for overall health and skin care.
In this article, Eikenbi invites you to explore detailed information about the horse placenta drink, its health benefits, and why this product has become a favorite choice for women who want to preserve their beauty.
What Is a Horse Placenta Drink?
A horse placenta drink is a dietary supplement made from extract derived from the placenta of a mare after birth. The placenta is the membrane that surrounds and nourishes the foal throughout pregnancy, supplying essential nutrients that support healthy development.
Harvesting horse placenta is not simple, and only a small percentage of horses meet the strict conditions required for collection. On average, a mare gives birth to one foal per year, with a pregnancy lasting nearly twelve months. As a result, the nutrients accumulated in horse placenta are often more abundant compared to other animals. Research has found that horse placenta contains high levels of natural protein, amino acids, and various vitamins, with a nutrient density that is rarely found in other mammals.
Thanks to modern manufacturing technology, this precious ingredient can now be extracted and refined into a convenient, easy to absorb liquid form. A horse placenta drink is not only recognized for its skin enhancing benefits but also for its positive effects on overall health. Many products on the market are also enriched with collagen, NMN, vitamins, and other supportive ingredients to enhance both wellness and beauty benefits.
The Current Trend of Using Horse Placenta Drinks
For centuries, placenta has been regarded as a premium beauty ingredient because of its rich nutrient profile. It contains high levels of growth factors, peptides, and proteins that stimulate the body’s production of collagen and elastin, two key components that determine skin elasticity and youthful appearance. In addition, placenta supports hormonal balance, helping women maintain vitality and beauty over time.
Today, horse placenta extract has become a common ingredient in many cosmetics and dietary supplements due to its outstanding health and beauty benefits. You can easily find products containing horse placenta in cosmetic stores, supermarkets, and pharmacies. With a wide range of product types and benefits, horse placenta drink products meet diverse health and beauty needs.
In Vietnam, products containing horse placenta are gaining popularity not only among women but also among men who are interested in improving their health and maintaining a youthful appearance.
Benefits of Horse Placenta Drink for Health and Beauty
Horse placenta is highly valued for its rich nutrient content and is considered a premium ingredient in high end beauty products. So what benefits does horse placenta collagen provide for health and beauty? Let’s take a closer look.
Brightens Skin and Slows Aging
Thanks to its high amino acid content, horse placenta helps stimulate natural collagen production, resulting in smoother skin, improved elasticity, reduced wrinkles, and a more youthful complexion. It also enhances skin hydration, promotes new cell regeneration, and helps regulate pigmentation, reducing dark spots, melasma, and freckles for a more even and radiant skin tone.
Regular use of a horse placenta drink may also help slow the aging process by supporting damaged cell repair and strengthening the skin’s defense against environmental stressors and UV exposure.
A study conducted on twenty nine women aged thirty to fifty nine showed that taking two hundred twenty milligrams of horse placenta extract daily for four weeks helped protect the skin from UV damage, stabilize melanin levels, and support protection against environmental aging.
Enhances Cell Regeneration and Recovery
Horse placenta contains essential nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, peptides, amino acids, and growth factors that help nourish the body, restore energy, and reduce fatigue. This makes it especially suitable for postpartum women, individuals caring for young children, or those experiencing stress and heavy workloads.
Natural growth factors such as EGF and FGF found in horse placenta also promote cell division and regeneration, helping repair damaged skin, fade scars and dark spots, and improve skin elasticity.
Strengthens the Immune System
A strong immune system is essential for protecting the body against illness. Horse placenta contains antibodies and growth factors that support immune function, helping the body fight bacteria, viruses, and other harmful agents. Daily supplementation with horse placenta may enhance resistance, improve immune health, and support faster recovery after illness.
Supports Hormonal Balance and Reproductive Health
In addition to beauty benefits, horse placenta extract can support reproductive health in both women and men. For women, horse placenta helps regulate hormones, reduce menstrual discomfort, stabilize cycles, and ease perimenopausal symptoms such as hot flashes, insomnia, and stress. Some studies suggest that placenta extract may contribute to hormonal balance and improved natural fertility.
For men, horse placenta may help boost vitality, support reproductive function, enhance endurance, and maintain energy levels. Supplementation may also contribute to improved sperm quality and reproductive health.
High Quality Horse Placenta Drink Products Today
The market currently offers a wide range of horse placenta drink products with varying quality and origins. Among them, Japanese horse placenta drinks are highly regarded by consumers for their effectiveness and strict production standards.
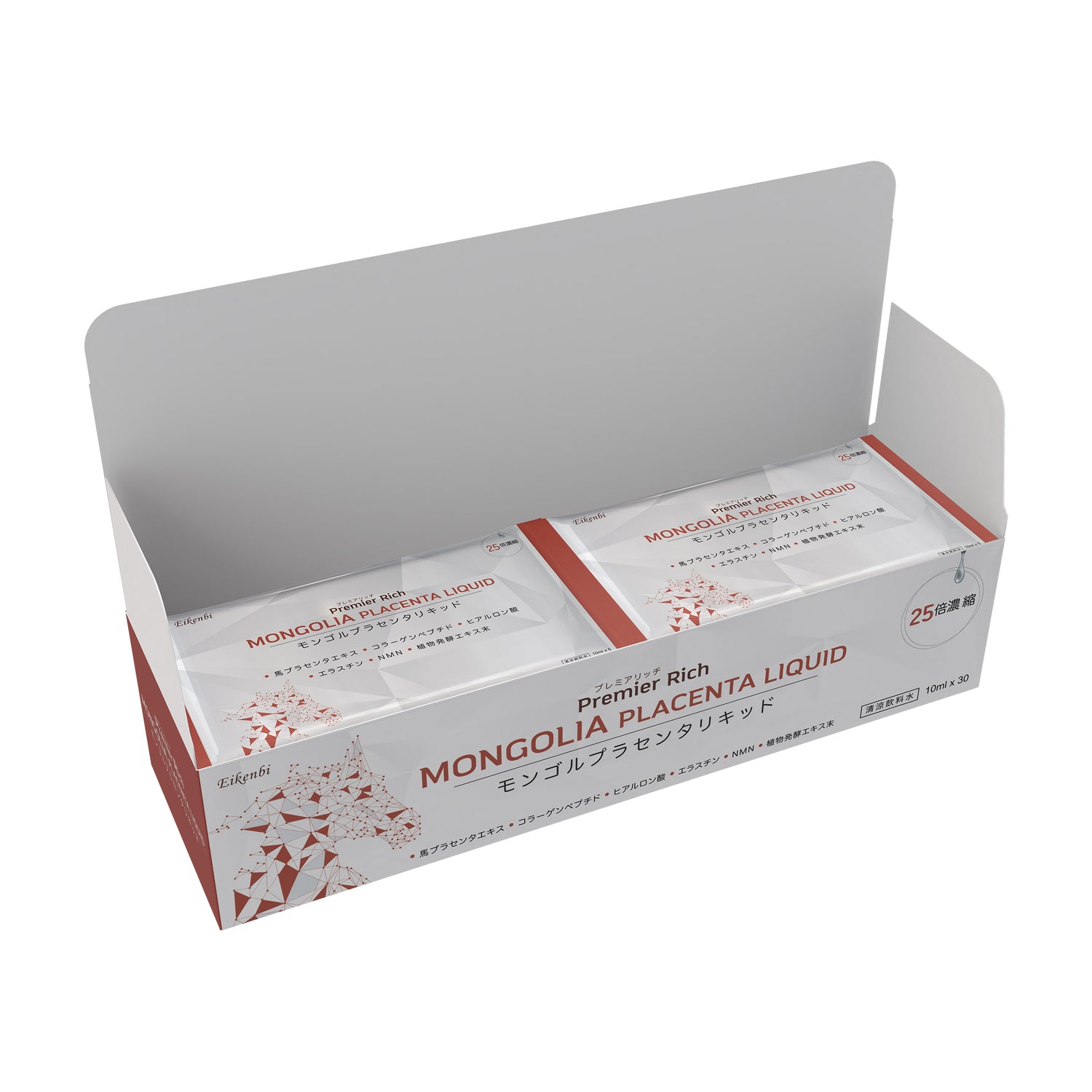
Mongolia Placenta Liquid Eikenbi is a premium product extracted from rare Mongolian war horse placenta, known for its purity and rich nutrient content. With up to nine thousand milligrams of horse placenta stem cell extract combined with collagen peptide, NMN, and other valuable ingredients, this product helps nourish the skin, improve hormonal balance, boost vitality, and restore energy. Its convenient liquid format makes it easy to use daily, helping you maintain radiant beauty from within and long lasting wellness.
Key ingredients: Nine thousand milligrams of Mongolian war horse placenta stem cells, collagen peptide, NMN, hyaluronic acid, fish elastin, and enzymes extracted from three hundred ninety types of vegetables and fruits.
Outstanding benefits
Improves skin elasticity and firmness, reduces wrinkles, and supports slowing the aging process.
Brightens skin, fades dark spots and pigmentation, and promotes a more even and radiant complexion.
Enhances immunity, restores physical strength, reduces fatigue, improves sleep, and increases daily energy.
Balances hormones, supports reproductive function, improves mood, reduces stress, and promotes overall wellness.
Criteria for Choosing a Quality Horse Placenta Drink
Horse placenta is becoming increasingly popular due to its impressive health and skin benefits. When choosing a horse placenta drink, it is important to prioritize reputable brands with strong market credibility to ensure product quality. Purchase from trusted distributors with clear origin information to avoid counterfeit or low quality products that could negatively affect your health.
There are several types of horse placenta available, including Hokkaido race horse placenta, purebred horse placenta, and Mongolian war horse placenta. When selecting a product, carefully review the type of placenta used, its origin, and whether the price aligns with market standards. Thorough research will help you accurately assess quality and avoid overpaying for products that do not match their value.
You should also pay attention to nutrient content. In addition to horse placenta, some products include collagen, hyaluronic acid, vitamins, royal jelly, or natural enzymes to enhance skin and health benefits.
Before making a purchase, read reviews from real users to understand the product’s effectiveness, taste, and safety profile. This will help you make a more informed decision and minimize unnecessary risks.
During use, follow the recommended dosage to reduce the risk of common side effects of horse placenta, such as digestive discomfort, mild rashes, breakouts, or bloating. If you have allergies or are taking medication, carefully review the ingredient list and consult a healthcare professional to ensure safe use.
Conclusion
With its impressive benefits for both health and skin, a horse placenta drink is truly an ideal choice for maintaining long term beauty and wellness. We hope that the product introduced in this article provides helpful information so you can select the option that best fits your needs.
If you are looking for premium Japanese health support products, visit Eikenbi.com to explore authentic Japanese domestic products. Contact us today for detailed consultation and personalized guidance.